Augmented Reality Enhanced Classroom
Grounded in two theoretical frameworks, AR provided enhanced learning in the classroom. Augmented Reality Enhanced Classroom.
This post has been reedited 4 May 2021.
This is a review of the article “Augmented Reality in The Classroom” written by Ayn Keneman, Associate Professor, and Racheal Waller.
Keneman earned awards in ISBE Early Childhood grant and the Excellence in Teaching award (2015) at National Louis University.
Their article reviews AR at the Smithsonian Institute (Washington, D.C.) National Technology Leadership Summit (NTLS).
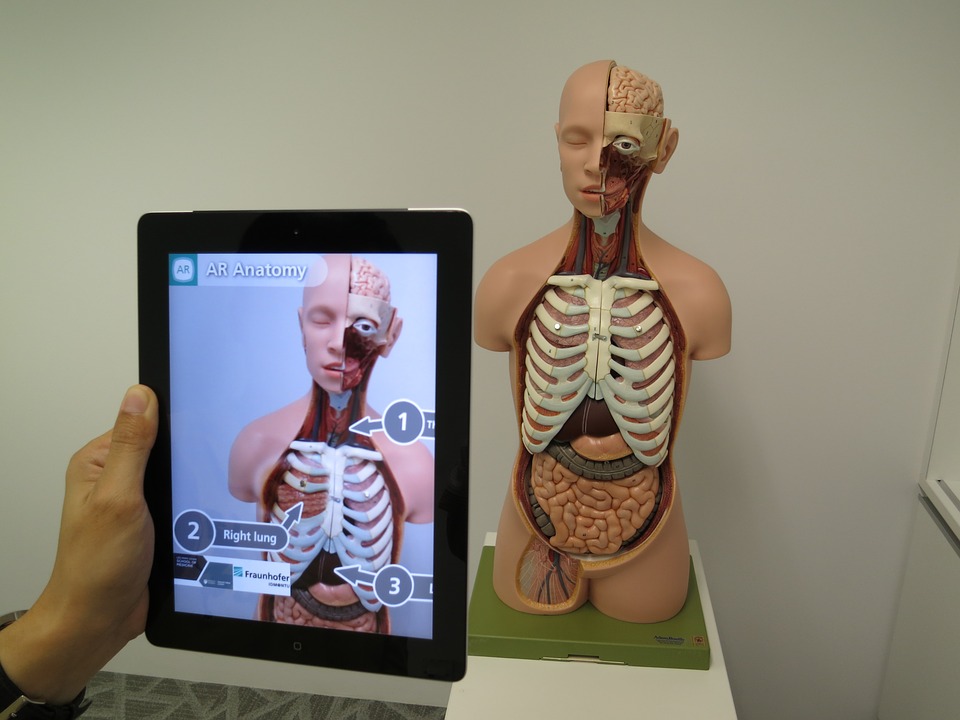
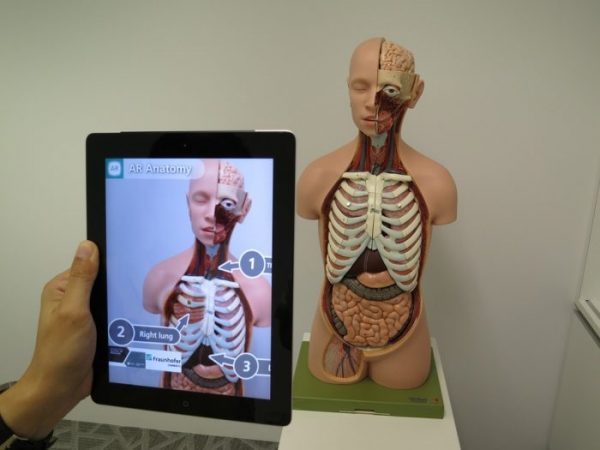
Moreover, the writers present their experience at the National Museum of Natural History using interactive and collaborative tools.
The exhibit, Skin and Bones, highlighted conversation and interaction with the AR application summarizing a transformative deeper experience.
Furthermore, students controlled their own learning using AR, this technique appeals to the Constructivist notion of learning.
The writers claimed an authentic experience on the field trip using AR technology.
Relying on social negotiation and intentional self-directed active learning, embedding AR engaged all the diverse learners. Claiming students build on prior knowledge through experiencing visual realities.
Concluding AR provided increased opportunities for expression through multiple literacy modalities. (Keneman &Waller, 2016)
Moreover, other references used in the article.
1) Situated learning theory and 2) Constructivist learning theory (Dunleavy and Dede (in press, p. 5).
Situated learning theory posits that all learning takes place within a specific context and the quality of the learning, interactions among the people, places, objects, process, and culture within and relative to the given context (Brown, Collins & Duguid, 1989).
Learning was a co-constructed participatory process in which all learners…“transformed through their actions and relations in the world” (Driscoll, 2000, p. 157).
Constructivist/Interpretivist theories of learning assume the meaning…imposed by the individual rather than existing in the world independently (Dede, 2008).
Knowledgeembedded in the setting in which itused, learning involves mastering authentic tasks in meaningful, realistic situations (Lave & Wenger, 1991).
AR technologies have high potential to raise student engagement (Dede, 2009); they student-centered and related to student interests, and thus allow students to be
Historically, there has been a “close connection between literacy, technology, and literacy instruction” (Karchmer, 2001, p. 442).
ARs can enhance the ability to communicate and can provide access to content experts in the field who live at a distance (Dunleavy, Dede, & Mitchell, 2009).
Learning situations…opportunity to adapt to learning situations to individual preferences and learning styles (Dunleavey, Dede, & Mitchell, 2009).
Augmented Reality Enhanced Classroom Learning





Add comment