Comparison Virtual Location Based AR Learning
This snapshot review of a peer-reviewed article exploring the author’s claimed areas, enhancing learning achievement, motivation, satisfaction, confidence, and spatial ability.
Showcasing how research into how student attitude was affected, cognitive load and understanding.
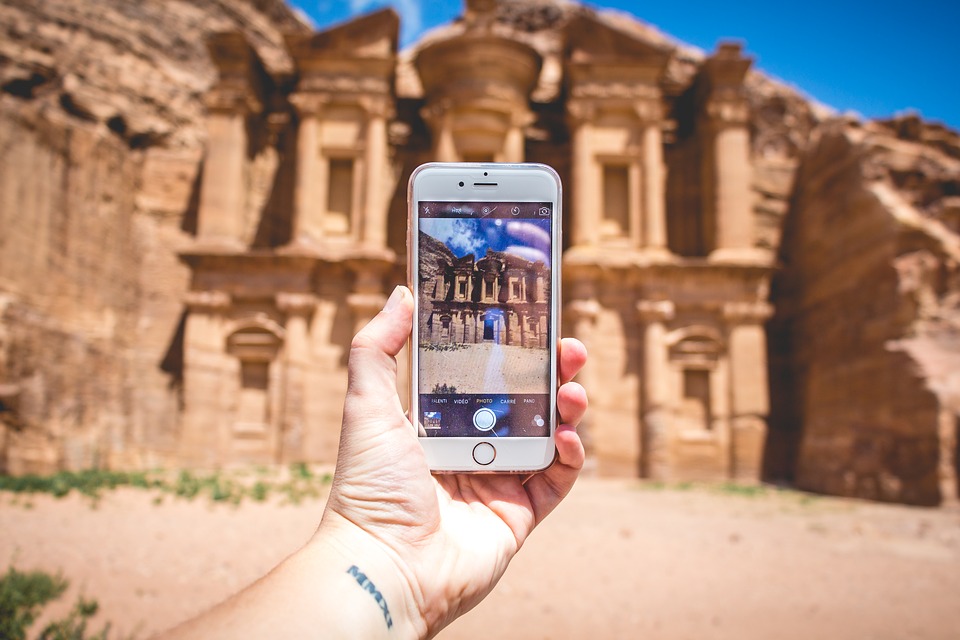

One study, Harley, Poitras, Jarrell, Duffy, and Lajoie, 2016, found participants’ emotions influenced outcomes during their ‘underpowered’ experiment (Harley et al., 2016).
They claimed a gap exists in learning settings and used a guided historical tour accessed by using mobile AR applications. Moreover, the total participants were thirty-one students limited from one North American university.
Two groups were surveyed. Comparing between both studies revealed students identified more differences outdoors and required less scaffolding to identify differences.
Participants reported high levels of enjoyment throughout both studies and less boredom in the outdoors. Further adding the results enhanced their understanding of AR applications’ effectiveness in different contexts virtual and location-based.
One weakness in the method was how the researchers were not concerned about generalizing to other populations in this article.






Add comment